Filtering Reports like a Pro
This article covers how to do advanced filtering within a report.
We recommend that you first familiarize yourself with creating reports in general before you dive into these topics. By the end of this article, you will know how to use reports to collect practically any information in ClassReach. So let’s get going!

General Tips to Get You Thinking:
- When pulling information from ClassReach, each result must match every filter that has been put into place. A filter for Last Names starting with “A” combined with a filter for Last Names starting with “B” will always return no results.
- The Users report allows you to report on any information collected by the User Info Form, and the Families report can report on any information from the Family Info Form. This is useful to know if you want to be able to report on something that isn’t currently tracked in ClassReach. Want to offer a subsidy to families at a certain income level? Adding a field for Income Range to the Family Info Form will allow you to create a Families report that can pull that information.
- In addition to being able to create an advanced filter for any type of custom report, there are also some built-in filters for each type of custom report. The Users report has an Active/Archived filter ready to go. The Form Responses report comes with a Submitted/Pending filter out of the box. The link in the previous bullet point can be used to see what filters are built-in to each report.
- You can always contact the ClassReach Support Team for help or advice on how to tackle a task!
The Six Types of Information and How to Compare Them:
I. Dates – A Date field includes information like Date Submitted, Birthday, or Date Created. The conditionals that can be applied to a Date are as follows:
- Is Equal to – This will then return results where the property’s date is the same date as the comparison date.
- Is Not Equal to – This then will return results where the property’s date is a different date as the comparison date.
- Is Before – This will then return results where the property’s date is chronologically before the comparison date.
- Is Not Before – This will then return results where the property’s date is not chronologically before the comparison date.
- Is After – This will then return results where the property’s date is chronologically after the comparison date.
- Is Not After – This will then return results where the property’s date is not chronologically after the comparison date.
II. Boolean – A Boolean is a True or False field, for example, fields like Is Archived or Is Enrolled. There are only two options with a Boolean, it is either True or it is False. The conditionals that can be applied to a Boolean are as follows:
- Is True – This will return results where the property’s value is set to true.
- Is True or Empty – This will return results where the property’s value is set to true or the field is empty and does not have a value.
- Is False – This will return results where the property’s value is set to false.
- Is False or Empty – This will return results where the property’s value is set to false or the field is empty and does not have a value.
- Is Empty – This will return results where the property’s value is empty and does not have a value.
- Is Not Empty – This will return results where the property’s value is not empty and does have a value.
III. Single Selection – A Single Selection is where one item from a list of possible values is selected. This would be fields like Relation to Student or Academic Level. A Single Selection will have a finite amount of choices, just like a Boolean, except the options can be anything, not just true or false. The conditionals that can be applied to a Single Selection are as follows:
- Is Equal to – This will return results where the property’s selected option is the same option as the comparison option.
- Is Not Equal to – This will return results where the property’s selected option is a different option than the comparison option.
- Is Empty – This will return results where the property is empty and does has not have an option selected.
- Is Not Empty – This will return results where the property is not empty and does have an option selected.
IV. Multiple Selection – A Multiple Selection is where multiple items from a list of possible values are selected. This would be fields like Roles. A Multiple Selection will have a finite amount of choices, just like a Boolean and Single Selection, except the options can be anything. The conditionals that can be applied to a Multiple Selection are as follows:
- Contains – This will return results where the property’s text has the entire comparison text contained within the text.
- Does Not Contain – This will return results where the property’s text does not have the comparison text contained within the text.
- Is Empty – This will return results where the property is empty and does not have a value.
- Is Not Empty – This will return results where the property is not empty and does have a value.
- Count Is Equal To – This will return results where the amount of entries in the property is equal to the comparison value.
- Count Is Not Equal To – This will return results where the amount of entries in the property is not equal to the comparison value.
- Count Is Less Than – This will return results where the amount of entries in the property is less than the comparison value.
- Count is Less Than or Equal To – This will return results where the amount of entries in the property is less than or equal to the comparison value.
- Count is Greater Than – This will return results where the amount of entries in the property is greater than the comparison value.
- Count is Greater Than or Equal To – This will return results where the amount of entries in the property is greater than or equal to the comparison value.
V. Numbers – A Number is a numerical entry that can have mathematics performed on it, so a phone number is not a number. This would be fields like Response Number, Age or Enrollment Count. The conditionals that can be applied to a Number are as follows:
- Is Equal to – This will return results where the property’s value is equal to the comparison value.
- Is Not Equal to – This will return results where the property’s value is not equal to the comparison value.
- Is Less than – This will return results where the property’s value is less than the comparison value.
- Is Not Less than – This will return results where the property’s value is not less than the comparison value.
- Is Greater than – This will return results where the property’s value is greater than the comparison value.
- Is Not Greater than – This will return results where the property’s value is not greater than the comparison value.
- Is Empty – This will return results where the property is empty and does not have a value.
- Is Not Empty – This will return results where the property is not empty and does have a value.
VI. Strings – A string is a text field or text area field. This would be a Name, Email or Phone Number. The conditionals that can be applied to a String are as follows:
- Is Equal to – This will return results where the property’s text is the same text as the comparison text.
- Is Not Equal to – This will return results where the property’s text is different text than the comparison text.
- Starts with – This will return results where the property’s text starts with the same text as the comparison text.
- Does Not Start with – This will return results where the property’s text starts with different text than the comparison text.
- Ends with – This will return results where the property’s text ends with the same text as the comparison text.
- Does Not End with – This will return results where the property’s text ends with different text than the comparison text.
- Contains – This will return results where the property’s text has the entire comparison text contained within the text.
- Does Not Contain – This will return results where the property’s text does not have the comparison text contained within the text.
- Is Empty – This returns results where the property is empty and does not have a value.
- Is Not Empty – This returns results where the property is not empty and does have a value.
Chaining Together Conditions:
You can link multiple conditions to a single selected property. Now let’s take a look at how the chained conditions are evaluated.
- And – When using And, both conditions must be met. A number is greater than 4 And less than 6, would allow only numbers that are 5 to show in the results. A date after June 6th And before Sept. 3rd would allow only dates that are Summer dates to show in the results.
- Or – When using Or, only 1 condition must be met, even if there are 47 conditions chained together, with Or only 1 has to match to allow the property to be in results. A string that contains an “A” Or contains an “E” Or contains an “I” Or contains an “O” Or contains a “U” would allow all strings that contain a vowel to show in the results.
Putting it All Together with an Example:
Ready to put all of this knowledge of filters into a practical application?
We are going to make use of some of those advanced filters that were discussed above. In this section of the documentation, we will create a custom Users report that will make use of those advanced filters to create a parent/teacher directory which includes mobile phone numbers and emails. We want to have a full directory of information, so we are also going to build 2 reports just to find out who doesn’t have this information filled out.

Who doesn’t have a phone number on file?
- Navigate to the Reports tab and click the + Report button to start a new report.
- Select the Users report.
- For this example, set Active Status to Active. This will only get the users who are currently at your school and will skip over users that have been archived.
- For Roles, select Guardian, Teacher and Admin. This will grab all the non-student users in the system.
- Click the Add a Filter… button and select Create Advanced Filter. In the Select a property to add a rule for drop-down select Mobile Phone. In the conditional check drop-down, change the selection from Is Equal to to Is Empty. This filter will now find all guardians, teachers and admins that do not have a mobile phone number on file. Click the Next button to proceed.
- In the Select a property to display drop-down, First Name, Last Name and Email would be useful fields. Click the Next button again.

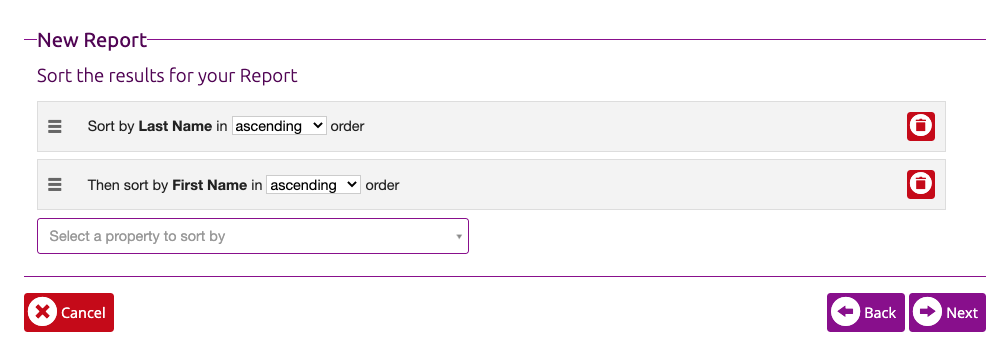
- On this screen, select Last Name and then choose ascending order since this would be the standard way to sort anything user related. Since we can expect to have multiple users with the same last name, it is a good idea to add another sort property, First Name and by ascending order as well. Click the Next button when you’re ready.
- For ease of use, select a Printable Web Page as the report format and click Next.

- Enter a name for your report, for example: “Users without a Mobile Phone Number”. Select Save and Run, and then click the green Save and Run button. Now you have a list of users that do not have a listed mobile phone number. You can regenerate a fresh report at any time by just clicking the Run button next to the report. Now to do the same for Email address.
Special Note: We are using two separate reports to find this information because of how filters work. If we tried to set up a single report to check for empty phone number and empty emails at the same time, it would only return users that are missing both phone number and email. This could be useful though if you would like to check to make sure each user has at least one form of contact on file and want a report to tell you who is lacking both. You’d simply set up both of the example advanced filters together on the same report.
Who doesn’t have an email address on file?
For this report, we are going to edit the first report we made instead of making an entirely new one.
- Navigate to the Reports tab and find the Users without a Mobile Phone Number report we just made. You can click the Users button on the left side to filter down to a list of only Users reports. Click the purple Edit button at the far right for our report.
- Active Status and Roles will stay the same here. Click the red Delete Rule to delete our Mobile Phone number filter. In the Select a property to add a rule for drop-down select Email. Set the conditional check drop-down selection to Is Empty again and click the Next button.

- Use the Select a property to display drop-down to add Mobile Phone to the list of fields. Then click the red Trash Icon next to Email to remove it. Click the Next button again.
- All of our sorting is still good to go, so just click the Next button.
- Printable Web Page is already selected so click Next.
- Change the name of your report. I changed mine to Users without an Email. Select Make a Copy, which will leave our original “Users without a Mobile Phone Number” untouched, and then click the green Save and Run button. Now you have a list of users that do not have a listed email address. You can regenerate a fresh report at any time by just clicking the Run button next to the report.

You now have a way to find all users without a mobile phone number and all users without an email address. The next report will be our directory that we originally set out to create.
- Navigate to the Reports tab and click the + Report button to start a new report.
- Select the Users report type on the left under the Custom heading.
- For this example, set Active Status to Active. This will only get the users who are currently using the system and will skip over users that have been archived.
- For Roles, select Guardian, Teacher and Admin. This will grab all the non-student users in the system. We do not need any additional filters for this report so you can go ahead and click the Next button now.
- In the Select a property to display drop-down, select First Name, Last Name, Cell Phone and Email and click the Next button again.
- For this report, select Last Name and then choose ascending order and add another sort property, First Name and by ascending order as well. Click the Next button.
- For ease of use, select a Printable Web Page as the report format and click Next.
- Enter a name for your report, I chose Parent and Teacher Directory for mine. Select Save and Run, and then click the green Save and Run button. Voila, a complete list of guardians, teachers, and admins that provides the standard contact information.
